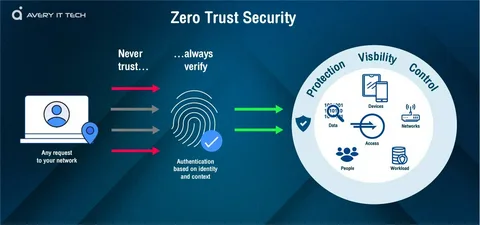
In an increasingly connected digital world, data security has never been more crucial. As cyber threats grow in terms of complexity and frequency, traditional perimeter-based security models no longer suffice. One of the most forward-thinking approaches to modern cybersecurity is Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). This model rests on a fundamental principle: never trust, always verify. Rather than assuming that users or systems inside a network are inherently trustworthy, Zero Trust requires continual authentication and validation.
With businesses relying heavily on data-driven decision-making and remote work models, implementing robust security frameworks is essential. Zero Trust Architecture is gaining popularity across industries, from finance and healthcare to education and government. In this environment, the demand for professionals trained in advanced data science and security techniques is escalating.
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust is not merely a single technology but a security framework that mandates strict identity verification for every single user and device attempting to actively access resources on a network, regardless of whether they are present inside or outside the network perimeter. The model assumes that threats can originate from both external and internal sources. This assumption forms the basis of its comprehensive authentication and access controls.
The core components of a Zero Trust framework include:
- Continuous Monitoring and Validation: Trust is never implicit. Every access request must be continuously evaluated using real-time data.
- Least Privilege Access: Users are given the minimum levels of access to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of insider threats.
- Device Access Control: Only authorised devices should be able to access network resources.
- Micro-segmentation: Networks are divided into small segments, limiting the lateral movement of threats.
- Encrypted Communication: Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest.
These principles make Zero Trust an ideal strategy in today’s multifaceted cyber threat landscape.
The Role of Data Science in Enabling Zero Trust
Data science plays an instrumental role in the successful implementation of Zero Trust. From analysing network traffic to identifying abnormal behaviour patterns, data science enables organisations to proactively detect and mitigate risks. Predictive analytics and machine learning models can actively forecast potential threats as per historical data and real-time metrics.
For example, anomaly detection algorithms can flag unusual user behaviours that deviate from the norm, such as access attempts at odd hours or data downloads of an unusual scale. These insights help security teams take pre-emptive actions, often before an actual breach occurs.
Professionals trained in data analysis, machine learning, and cybersecurity are well-equipped to contribute to these systems. Enrolling in a data scientist course can provide a solid foundation for building and fine-tuning these intelligent monitoring tools. Such courses typically cover statistical modelling, machine learning, data visualisation, and big data handling—skills that are directly applicable to Zero Trust environments.
Hyderabad as a Data Science and Cybersecurity Hub
As India’s technology sector continues to expand, Hyderabad is emerging as a key centre for data science and cybersecurity education and employment. The city’s robust IT infrastructure, coupled with the presence of global tech companies and research institutions, makes it an ideal environment for aspiring data professionals.
Enrolling in a data science course in Hyderabad offers students a highly unique blend of theoretical knowledge and industry exposure. Many institutions collaborate with leading cybersecurity firms to provide hands-on experience in real-world scenarios. This is especially relevant for students interested in implementing or supporting Zero Trust frameworks within enterprises.
Hyderabad-based programmes often incorporate modules in network security, ethical hacking, and risk analysis, allowing students to understand how data science intersects with secure system design. These interdisciplinary courses prepare graduates for high-demand roles in cybersecurity operations, threat intelligence, and data governance.
Implementing Zero Trust in Real-World Scenarios
The journey toward Zero Trust is incremental and must be tailored to an organisation’s particular needs. Here are some real-world scenarios where Zero Trust proves invaluable:
- Remote Workforces: With employees accessing systems from various locations and devices, traditional VPNs are not sufficient. Zero Trust ensures that every access request is scrutinised, reducing the likelihood of breaches.
- Cloud Environments: As businesses shift to cloud-based infrastructures, ensuring secure access becomes complex. Zero Trust frameworks work well with cloud-native technologies, offering scalable security solutions.
- Healthcare Systems: Patient data is highly sensitive and must be protected from both external hackers and internal mishandling. Zero Trust ensures that only verified personnel can access specific information, with each access logged and analysed.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and fintech companies store massive amounts of personal and transactional data. Implementing Zero Trust can significantly reduce fraud risk and compliance violations.
Each of these sectors benefits from skilled professionals who understand the confluence of data science and cybersecurity. With Zero Trust gaining traction, expertise in this domain is becoming a significant career advantage.
Challenges in Adopting Zero Trust
Despite its many benefits, transitioning to a Zero Trust model comes with challenges:
- Legacy Systems: Older infrastructure may not support modern authentication protocols or monitoring systems.
- Cultural Resistance: Employees and even IT teams may resist changes in access control policies and workflows.
- Complex Integration: Integrating Zero Trust principles into existing systems requires careful planning and may involve initial costs.
- Skill Gaps: Many organisations lack personnel with the required skill sets in data analytics and cybersecurity to effectively implement and manage Zero Trust systems.
These challenges highlight the importance of education and upskilling. By undertaking a comprehensive data scientist course, professionals can acquire the interdisciplinary knowledge needed to bridge the gap between traditional IT and modern security paradigms.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Architecture showcases a paradigm shift in how we approach cybersecurity. By treating all users and devices as untrusted by default and continuously verifying their legitimacy, it creates a resilient and adaptive security posture. The successful implementation of this specific model relies heavily on data science techniques such as behavioural analytics, machine learning, and real-time data monitoring.
For professionals looking to enter or advance in this field, pursuing specialised education is vital. Whether through a general course or a regionally focused data science course in Hyderabad, acquiring these skills provides the tools necessary to build secure, data-driven organisations. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the need for intelligent, proactive security strategies like Zero Trust will only grow stronger.
The future of data security lies not just in better technology, but in smarter people—trained to harness the power of data to build safer digital environments for all.
ExcelR – Data Science, Data Analytics and Business Analyst Course Training in Hyderabad
Address: Cyber Towers, PHASE-2, 5th Floor, Quadrant-2, HITEC City, Hyderabad, Telangana 500081
Phone: 096321 56744